Skin Cancer Screening
Embark on a journey of aesthetic excellence with The Naderi Center. Experience unparalleled artistry and precision for transformative beauty.
Ensure Your Health with the Benefits of Skin Cancer Screening
Skin Cancer Screening, a vital step towards health vigilance, paves the way for early detection and timely intervention. At The Naderi Center, we believe in the power of proactive care, ensuring our patients stay ahead in the journey of health and well-being under Dr. Naderi’s expert guidance.
Early Detection
Spot potential issues before they escalate, maximizing treatment success.
Peace of Mind
Regular screenings alleviate concerns, providing assurance in your skin's health.
Guided Expertise
Benefit from Dr. Naderi's precision and knowledge, ensuring comprehensive and accurate evaluations.



Skin Cancer Screening at The Naderi Center
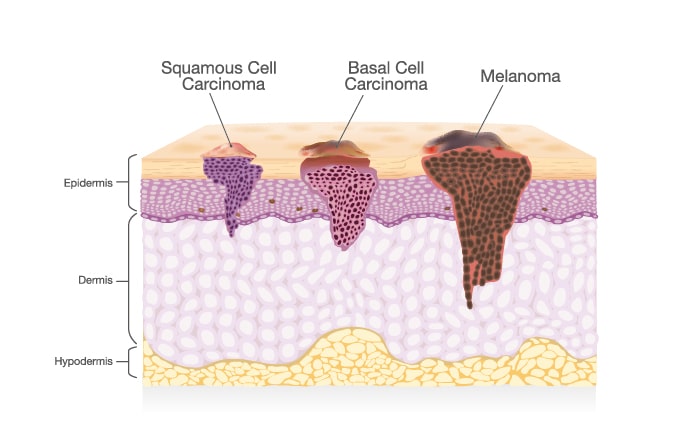
Diagnosing Types of Skin Cancer
What Does Skin Cancer Look Like?
The different forms of skin cancer may appear similar to other conditions of the skin, like eczema or psoriasis, and should only be diagnosed by a board-certified dermatologist. In some cases, a spot may appear on otherwise normal skin, and in other cases, a mole may change.
Some changes that might be indicative of skin cancer are:
- A sore or itchy skin lesion
- A lump on the skin or around facial features like the eyes, nose, and ears
- A discolored patch of skin, often pink, red, or brown
- A dark streak noticeable below a fingernail or toenail
- Injury to the skin without trauma that bleeds
- Crusting of the skin that will not heal
The affected areas may be small or large in size, depending on which type of the disease is developing. Not all skin cancers develop in commonly sun-exposed areas, but lesions are more likely to be found in these locations. With early discovery by Dr. Snodgrass during an annual skin cancer screening, patients are more likely to receive successful treatment for the disease with minimal damage to the skin.
Symptoms of Skin Cancer
Aside from changes in the skin itself, skin cancer can cause other symptoms. Skin cancer that has grown deep into the skin may begin to affect the nerves, causing a tingling, burning, or a numb sensation.
Much like other types of cancer, skin cancer may cause noticeable tumors below the skin, though not all tumors are visible. Advanced cancer may cause a patient to feel weak or tired if it has spread to other areas of the body.
How is skin cancer diagnosed?
Skin cancer screenings involve a dermatologist examining for any lesions or discolorations in the skin that are suspicious for cancer. During a procedure known as a biopsy, a dermatologist removes a portion of the suspect tissue, which is then sent to a laboratory. A slide is created and a pathologist, a doctor who studies disease processes, reviews the tissue to make a diagnosis. In some cases, more testing of the sample or the patient’s skin is required.
Types of skin cancer
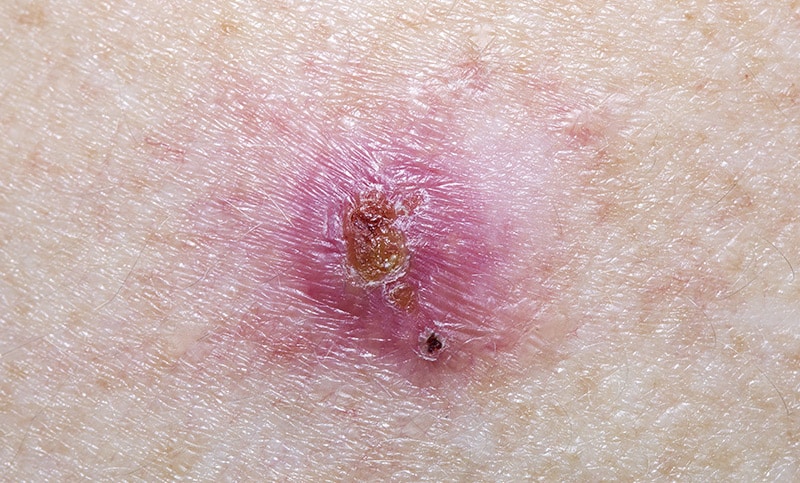
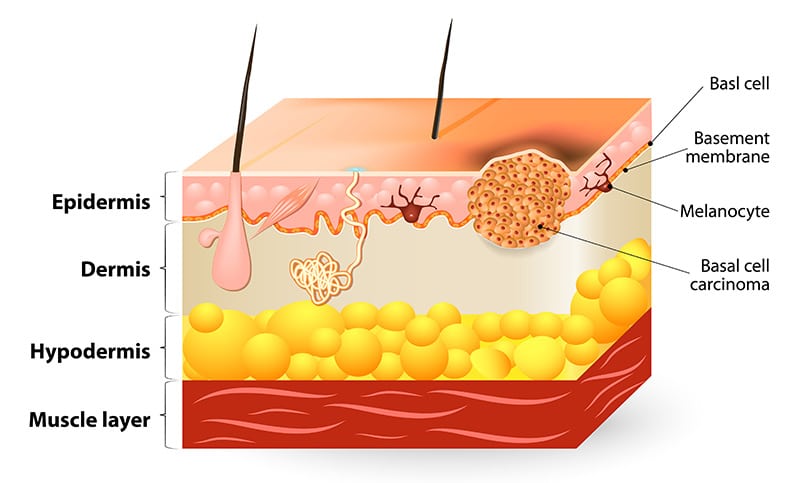
Basal Cell Carcinoma
The most common type of skin cancer is basal cell carcinoma (BCC). This type of cancer originates from the basal cells of the skin’s outermost layer, the epidermis, forming its foundation.
This form of skin cancer is typically found on areas of the face and body that might be repeatedly exposed to the sun, like the face, neck, and back. The first signs of the emerging disease are flesh-colored or pink bumps that appear shiny and can occur in individuals as young as their 20s or 30s.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The second most prevalent form of skin cancer is squamous cell carcinoma, abbreviated as SCC. Squamous cells form from the second layer of cells found in the epidermis. Squamous skin cells are located near the skin’s surface. This type of carcinoma often appears irregularly shaped, pink, and scaly in areas like the lips and body.
Dental specialists should also screen for squamous cell carcinoma, which can occur inside the mouth. It is more likely that patients who are middle-aged or older will be diagnosed with SCC.
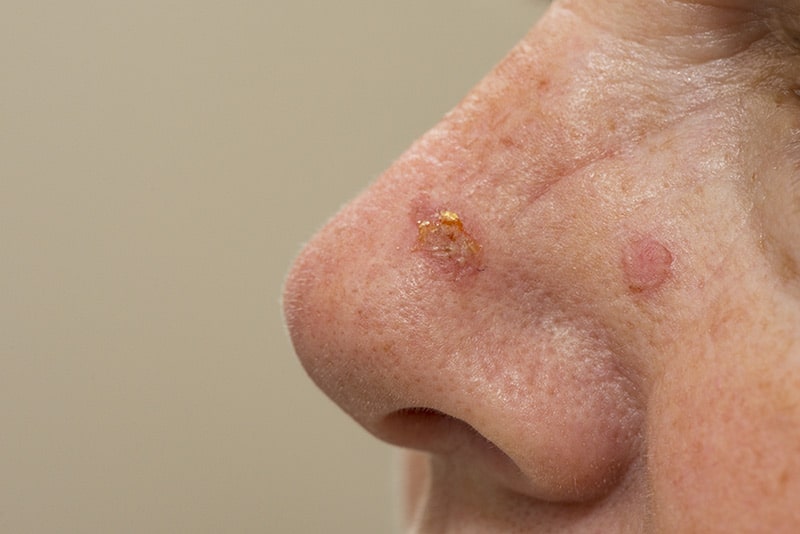
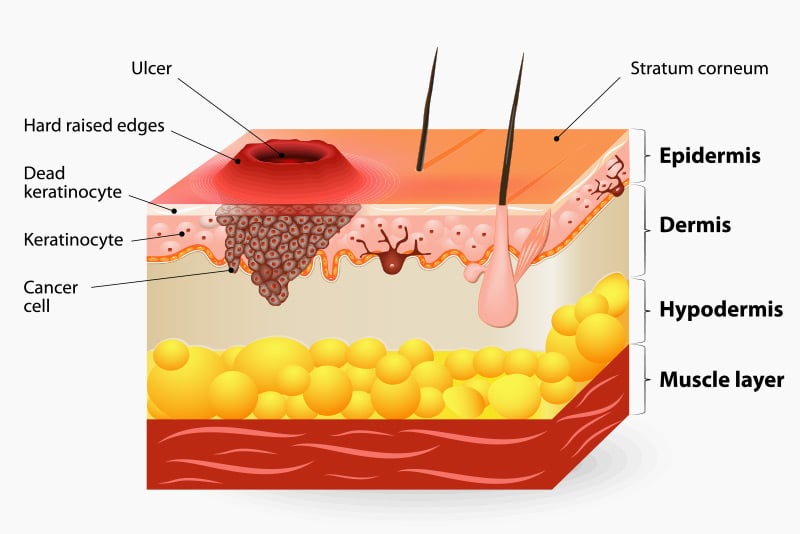
Malignant Melanoma
Most deaths from skin cancer are attributed to melanoma, which is an aggressive form of the disease that begins in the melanocytes, or mature cells that form skin pigment. Malignant melanoma can appear acutely as an independent lesion or it can form from existing moles that display changes like an irregular shape, sudden itching, or bleeding.
When discovered early, melanoma can be successfully treated but when left to develop, it can metastasize, or spread, to other tissues with higher fatality rates. Most cases of melanoma are diagnosed at around age 60. Research suggests that sunburns and tanning beds contribute to the formation of this type of skin cancer.
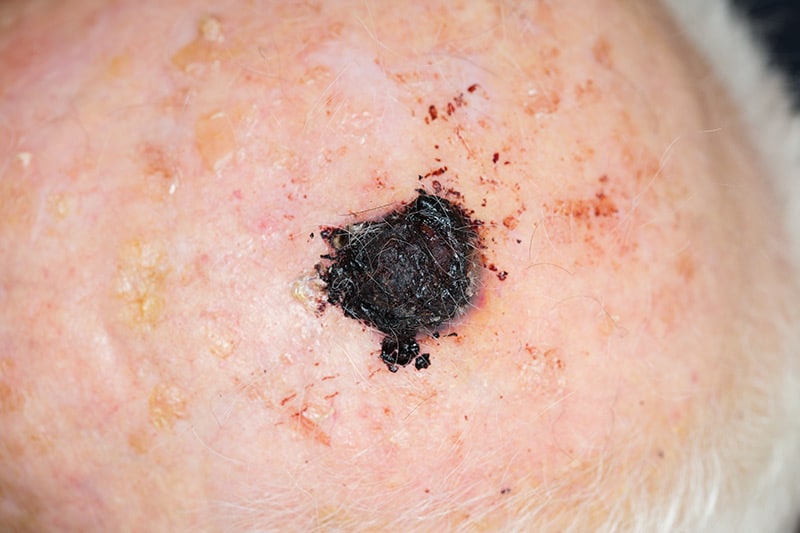
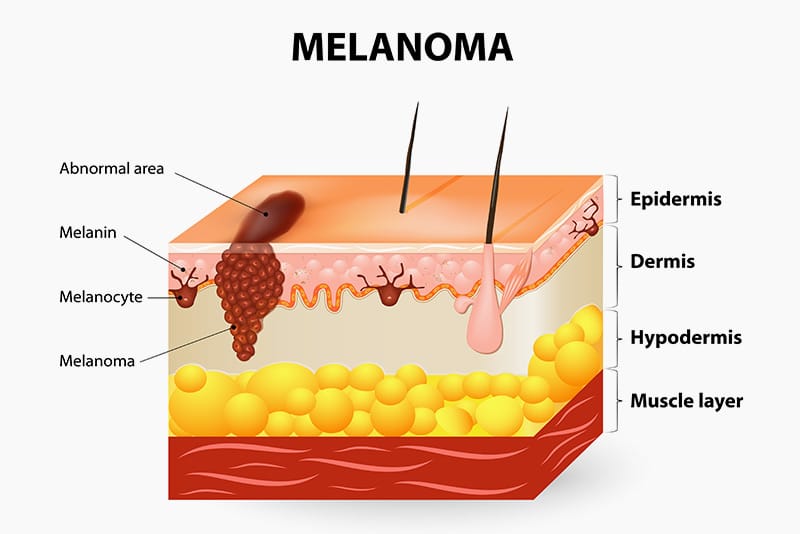
Less Common Skin Cancers
Most skin cancer will be diagnosed as basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, or malignant melanoma, but other types of the disease exist. Less common skin cancers include:
- Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma (CTCL) – a blood cancer that begins in the skin cells
- Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans (DFSP) – a slow-growing type of cancer that forms from the mid-layer of skin
- Merkel Cell Carcinoma – a rare and aggressive skin cancer
- Sebaceous Carcinoma – skin cancer that develops in sebaceous (oil glands), most commonly around the eyes
Dr. Snodgrass can explain these rare forms of skin cancer during the dermatological consultation if the patient is at risk or displays any associated changes in the skin.
Skin Cancer Prevention
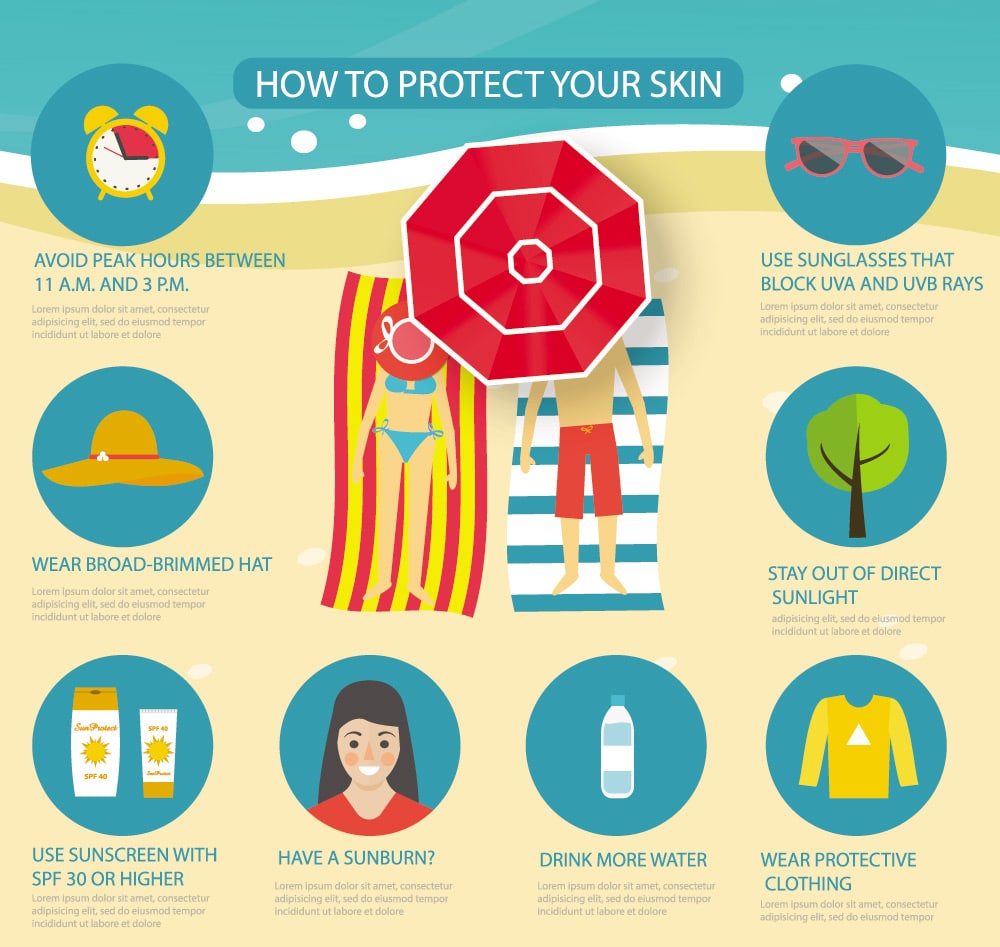
Top 10 Guidelines for Preventing Skin Cancer
- Avoid sun burns or tanning
- Apply minimum of 30 SPF with UVA and UVB protection, and reapply every 90 minutes
- Wear protective clothing
- Wear broad-brimmed hats
- Avoid sun at peak hours: 11 AM – 3 PM
- Seek shade when possible
- Use sunglasses to block UVA and UVB rays
- Avoid tanning beds
- Exam your skin monthly
- Visit the dermatologist for annual skin checks
Testimonial
“The Naderi Center has an amazing team of professionals! They are so knowledgeable and recommend services/products that are perfect for you. They really took the time to listen to my concerns and answered all my questions. Highly recommend!”
SE
SPF for Skin Cancer Prevention
SPF stands for sun protection factor and prevents damage from cancer-causing UV rays. SPF is measured by the amount of time it takes for a person to be affected by sun exposure; for example, SPF 15 works to prevent damage, like a sunburn, for up to 15 times longer than the amount of protection the natural skin provides.
A sunburn is a form of radiation burn on the skin, while a tan is created by the skin’s defense against these burns. By creating a darker skin tone, UV rays cannot penetrate as easily, preventing excess damage to the skin’s DNA. Whether the skin turns pink or tan, either color is evidence of skin damage.
Sunscreen and sunblock contain SPF while tanning lotions and oils do not. Tanning deliberately in the sun or subjecting the skin to the concentrated UVA and UVB rays from tanning beds can cause patients to develop premature signs of aging and make the skin more likely to develop cancer cells.
Salons and gyms that feature tanning facilities often require users to sign a waiver stating they understand the risks to their health. Dermatologist, Dr. Alexandra Snodgrass, works to educate her Virginia and Chevy Chase, MD patients on the dangers of this activity.
Skin Cancer Treatment
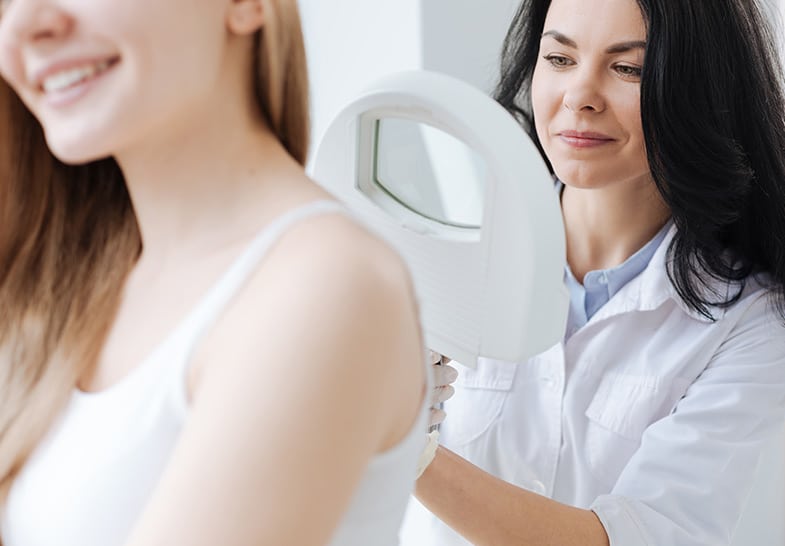

Skin Cancer Screening
During a skin cancer examination, the patient will change into an exam gown and the doctor may inquire about whether he or she has noticed any changes to existing moles or observed any new growths in the skin over the past year. Dr. Snodgrass will also ask about the patient’s use of sun protection in the past and present.
Those who have a fair complexion or a history of unprotected sun exposure are at greater risk of developing the disease. Dr. Snodgrass will complete a facial and body exam as needed by surveying the patient’s skin, including hidden areas like the scalp, behind the ears, and even the soles of the feet.
Visual inspection can be performed alone or alongside special techniques that employ light of varying wavelengths and ultraviolet (UV) photos, which help the doctor to view underlying changes in the skin. If melanoma is suspected, Dr. Snodgrass can perform a biopsy under local anesthesia, which will extend the appointment an additional 15-30 minutes per site.
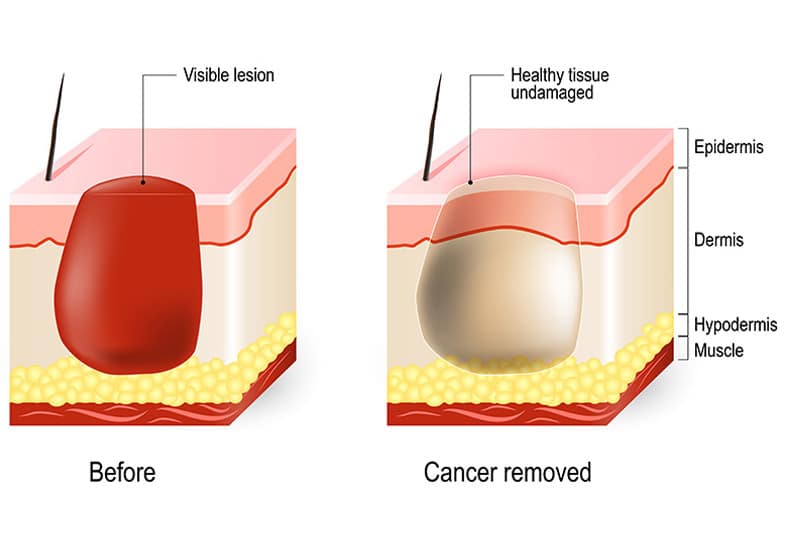
Treatment for skin cancer
Most minor skin-cancer lesions are treated topically and may be excised surgically, frozen off during cryotherapy, destroyed with electrodesiccation, or removed with laser phototherapy during an in-office procedure. These procedures may not be sufficient for more extensive areas of damage and patients might be referred to a Mohs surgeon for a more in-depth treatment.
During the Mohs procedure, the surgeon removes one layer of the lesion and surrounding skin at a time, visualizing each section of tissue, until all the cancerous cells are eliminated. In other cases, patients may be referred to an oncologist for a treatment regimen that can include medication, radiation, and chemotherapy treatments. Newer methods like biological therapy can also be used to leverage the body’s own defense system to target cancerous cells.
Skin Cancer Screening performed by Dr. Alexandra Snodgrass
The Naderi Center of offers yearly skin cancer screenings in an effort to proactively address patients’ health concerns and to prevent the spread of the disease. The experts at the center all specialize in different procedures and offer medical and cosmetic intervention as needed. In-house Board Certified dermatologist, Dr. Alexandra Snodgrass, specializes in skin health and can treat skin cancer while maintaining the patient’s aesthetics.
Known as a leader in skincare and cosmetic procedures, The Naderi Center has been serving patients in the Virginia, Maryland, and Washington D.C. area for more than 10 years. The Naderi Center is known for being the source of physicians and surgeons that are specialized in their realm and scope of practice. Patient’s come to The Naderi Center when they want an expert on the procedure or condition they are trying to improve. Contact one of The Naderi Center’s two offices for more information, or to schedule your skin cancer screening. A patient coordinator can be reached at our Reston, Virginia office at 703-481-0002 and at our Chevy Chase, Maryland office at 301-222-2020.

Skin Cancer Screening FAQs
What Skin Cancer Screening office is near me?
If you live in the states of Virginia or Maryland, The Naderi Center for Plastic Surgery and Dermatology offers skin cancer screening among its services. For a full list of services, please visit our Locations page.